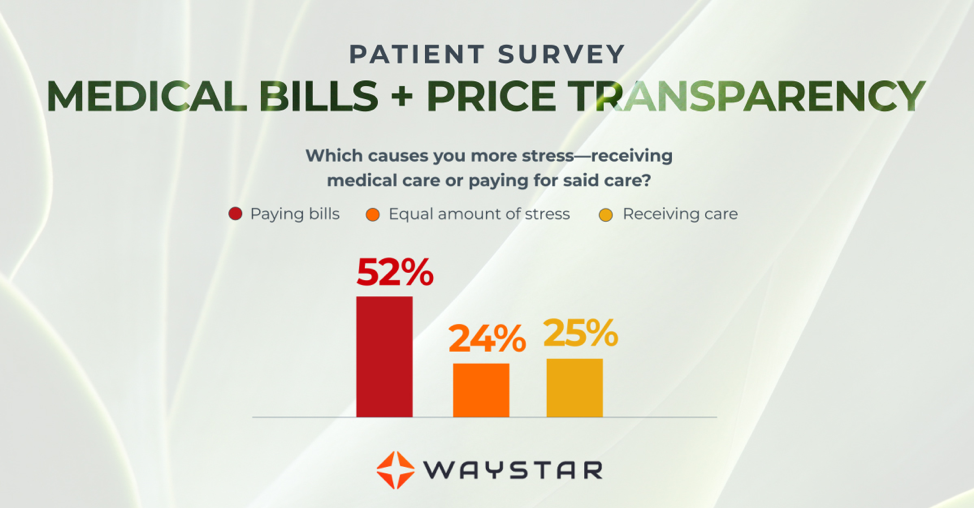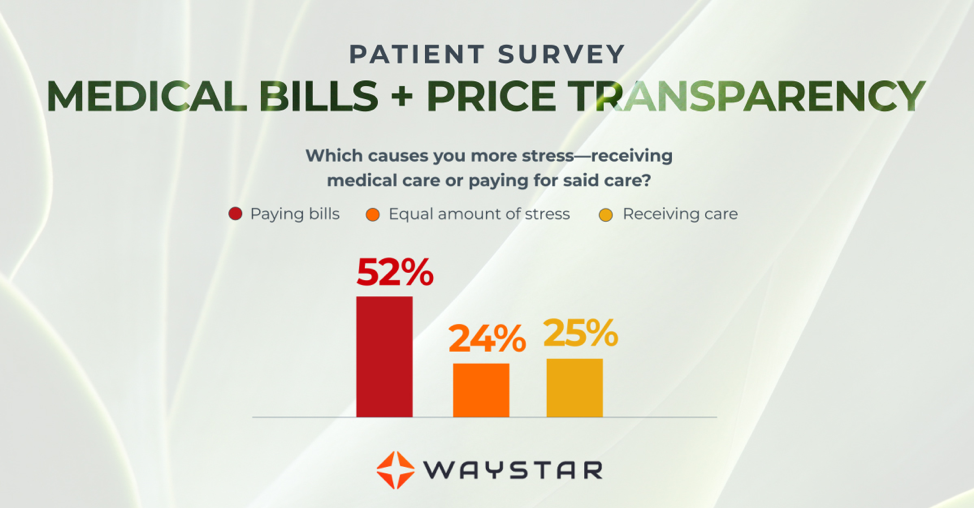
Mar 10, 2021 | Medical Billing Software Blog, Partner, Waystar
New Patient Survey About Price Transparency Rule
With the cost of insurance premiums and deductibles both on the rise, patients have begun taking on greater responsibility for paying for healthcare than ever before. In return, they are becoming more discerning shoppers and expect more from the patient experience that their providers are delivering. One of the biggest steps that have been taken to create a more standardized, consumer-like experience is the introduction of the final price transparency rule from the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services.
More than half of consumers have received an unexpected medical bill
Despite the $3.81 trillion that was spent on healthcare in 2019, America’s healthcare payments system has long remained opaque and broken. Patients are frequently faced with unexpected or surprisingly high medical bills, discover too late that a provider they’d been told was in-network was actually out of network, and are forced to wait 60-90 days to receive their medical bills.
Patients are more concerned about billing than the quality of care
In October 2020, Waystar surveyed 1,000 consumers about their experiences with medical bills, and awareness and attitudes towards the upcoming price transparency rule. More than half of respondents have received an unexpected medical bill, meaning that they assumed a service was covered by insurance and it ultimately was not, or the amount they expected to pay out of pocket was different from the bill they received.
> > > CLICK HERE To Read the Results of the Waystar Survey < < <
ABOUT EZCLAIM:
EZClaim is a medical billing and scheduling software company that provides a best-in-class product, with correspondingly exceptional service and support. Combined, they help improve medical billing revenues. To learn more, visit EZClaim’s website, e-mail them, or call them today at 877.650.0904.
[ Article contributed by Waystar ]
Nov 10, 2020 | Medical Billing Software Blog, Partner, Revenue, Support and Training, Waystar
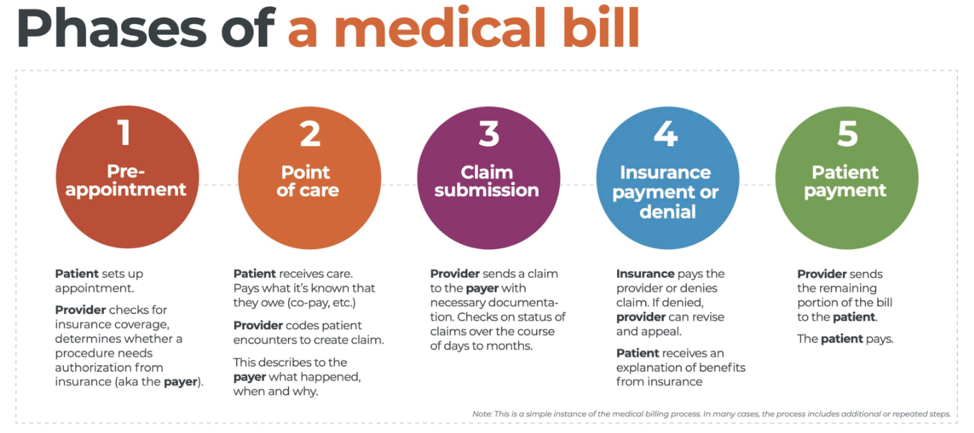
 There are five ‘phases’ in the life cycle of a medical bill: Pre-appointment; Point of care; Claim submission; Insurance payment or denial; and Patient payment. This post will overview each of these phases, and could even be considered to be a “101-level” course on Revenue Cycle Management.
There are five ‘phases’ in the life cycle of a medical bill: Pre-appointment; Point of care; Claim submission; Insurance payment or denial; and Patient payment. This post will overview each of these phases, and could even be considered to be a “101-level” course on Revenue Cycle Management.
With high deductible health plans on the rise, the recent explosion of telehealth appointments due to COVID-19, and many other factors in play, it’s more important than ever for everyone to understand the life cycle of a medical bill, and how the process works. The healthcare revenue cycle is relevant not only to those who work in healthcare, but to the patient, too.
The revenue cycle is the series of processes around healthcare payments—from the time a patient makes an appointment to the time a provider is paid—and everything in between. One way to think of it is in terms of the life cycle of a medical bill. Although there are many ways this process can play out, this post will lay out a common example below:
1. Pre-appointment
For most general care, the first stage of the revenue cycle begins when a patient contacts a provider to set up their appointment. Generally this is when relevant patient information will begin to be collected for the eventual bill, referred to on the financial side of healthcare as a claim.
At this point a provider will determine whether the appointment and procedure will need prior authorization from an insurance company (referred to as the payer). Also, the electronic health record (EHR) used to help generate the claim is created, and will begin to accumulate further detail as the provider sends an eligibility inquiry to check into the patient’s insurance coverage.
2. Point of care
The next step in the process begins when the patient arrives for their appointment. This could include when a patient arrives for an initial consultation, an outpatient procedure, or for a follow-up exam. This could also include a Telehealth appointment.
At any of these events, the provider may charge an up-front cost. One example of this is a co-pay, which is the set amount patients pay after their deductible (if they are insured), however, there are other kinds of payments that fall into this category, too.
3. Claim submission
After the point of care, the provider completes and submits a claim with the appropriate codes to the payer. In order to accomplish that, billing staff must collect all necessary documentation and attach it to the claim. After submitting the claim to the payer, the provider’s team will monitor whether a claim has been been accepted, rejected, or denied.
[ Note: Medical coding refers to the clerical process of translating steps in the patient experience with reference numbers. The codes are normally based on medical documentation, such as a doctor’s notes or laboratory results. These explain to a payer how a patient was diagnosed and treated, and why. This information helps the payer decide how much of an encounter is covered under any given insurance plan, and therefore how much the payer will pay. ]
4. Insurance payment or denial
Once the payer receives the claim, they ensure it contains complete information and agrees with provider and patient records. If there is an error, the claim will be rejected outright and the provider will have to submit a corrected claim.
The payer then begins the review process, referred to as adjudication. Payers evaluate claims for accurate coding and documentation, medical necessity, appropriate authorization, and more. Through this process, the payer decides their financial obligation. Any factor could cause the payer to deny the claim.
If the claim is approved, the payer submits payment to the provider with information explaining details of their decision. If the claim is denied, the provider will need to determine if the original needs to be corrected, or if it makes more sense to appeal the payer’s decision.
Following adjudication, the payer will send an explanation of benefits (EOB) to the patient. This EOB will provide a breakdown of how the patient’s coverage matched up to the charges attached to their care. It is not a billing statement, but it does show what the provider charged the payer, what portion insurance covers, and how much the patient is responsible for.
5. Patient payment
The next phase occurs when the provider sends the patient a statement for their portion of financial responsibility. This stage occurs once the provider and payer have agreed on the details of the claim, what has been paid, and what is still owed.
The last step occurs when a patient pays the balance that they owe the provider for their care. Depending on the amount, the patient may be able pay it all at once, or they might need to work with the provider on a payment plan.
The above example represents one way the lie cycle of a medical bill can play out. Some of the ‘phases’ are often repeated. Because of the complexity of healthcare payments and the parties involved, there is not always a ‘straight line’ from patient care to complete payment. That’s why we call it the revenue cycle, and there are companies that provide systems for its management.
One of EZClaim’s partners, Waystar, aims to simplify and unify healthcare payments. Their technology automates many parts of the billing process laid out above, so it takes less time and energy for providers and their teams, and is more transparent for patients (Click here to learn more about how Waystar automates manual tasks and streamlines workflows.) When the revenue cycle is operating at its most efficient, providers can focus their resources on improving patient care—and that’s a better way forward for everyone!
For more information of how Waystar works together with EZClaim, click here.
[ Article and image provided by Waystar ]
———————————-
ABOUT EZCLAIM:
EZClaim is a medical billing and scheduling software company that provides a best-in-class product, with correspondingly exceptional service and support, and can help improve medical billing revenues. To learn more, visit their website, e-mail them at sales@ezclaim.com, or call a representative today at 877.650.0904.

Aug 11, 2020 | Medical Billing Software Blog
The most important thing a medical practice can do for their financial health is collecting payments from patients. So, because patients are not usually savvy when it comes to the nuts and bolts of their contract, they become frustrated when you send them a bill and, beginning on January 1st, your office staff get inundated with the question, “Why do I have a balance?”
“Approximately 68% of patients with bills of $500 or less did not pay off the full balance during 2016—up from 53% in 2015 and 49% in 2014.” Source: Patients May be the New Payers, But Two in Three Do Not Pay Their Hospital Bills in Full, TransUnion Healthcare, June 26, 2017
So, let’s make sure your office is equipped and able for collecting payments from patients for the services you rendered, rather than them becoming a part of this scary statistic.
Let’s begin with the basics: Make sure that your staff understands these key terms, and is comfortable explaining them to your patients.
Deductible: The deductible is the amount the patient has to pay for covered services before the insurance plan pays. Some insurance plans will apply an office visit to the deductible, others will not. Family plans typically have an individual and family deductible.
Copay & Coinsurance: These are both the portion the patient will be responsible for after their deductible has been met. Copays are a set, flat fee. Coinsurance is a set percentage that the patient will pay.
Maximum Out-of-Pocket: This is the limit of what a patient will pay for covered services within a plan year. Again, on family plans, there may be an individual max and family max.
Now, keep in mind that your staff will not know the details of your patients’ plans, nor should they be expected to! In the ever-changing world of health insurance, patients need to become better consumers. So, just being able to explain these key terms and why they create a patient balance will help them become better insurance plan shoppers!
Use your tools. Look into using Integrated Eligibility (available through your billing software and your clearinghouse). This will allow your staff to check remaining deductible balances, copay, and coinsurance amounts with the click of a button. These results allow practices to confidently collect at the time of service rather than spending time and money on sending statements and working to collect after the visit.
In addition to that, create a plan and stick to it. Use this time to review the efficiency of your patient collections plan. Are you using an outdated plan or policy? Have you considered offering payment plans to patients with an HSA card kept on file? Make sure that your employees understand how important patient collections are to the practice, educate them on the plan, and support them when they hold patients accountable to the patient collections policy.
For more information on how EZClaim can help you with this journey, schedule time with our sales team. Or, if you ready to get started right now, then download your FREE 30-day demo today!
[ Written by Stephanie Cremeans of EZClaim ]