Nov 10, 2020 | Medical Billing Software Blog, Partner, Revenue, Support and Training, Waystar
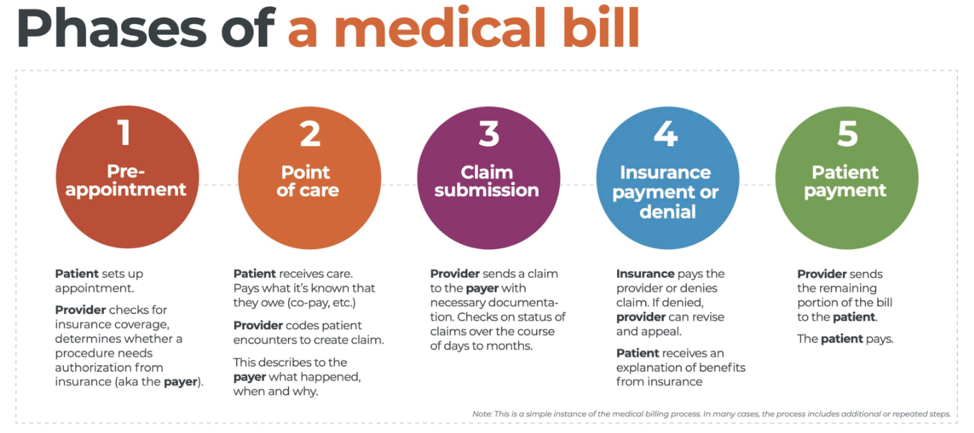
 There are five ‘phases’ in the life cycle of a medical bill: Pre-appointment; Point of care; Claim submission; Insurance payment or denial; and Patient payment. This post will overview each of these phases, and could even be considered to be a “101-level” course on Revenue Cycle Management.
There are five ‘phases’ in the life cycle of a medical bill: Pre-appointment; Point of care; Claim submission; Insurance payment or denial; and Patient payment. This post will overview each of these phases, and could even be considered to be a “101-level” course on Revenue Cycle Management.
With high deductible health plans on the rise, the recent explosion of telehealth appointments due to COVID-19, and many other factors in play, it’s more important than ever for everyone to understand the life cycle of a medical bill, and how the process works. The healthcare revenue cycle is relevant not only to those who work in healthcare, but to the patient, too.
The revenue cycle is the series of processes around healthcare payments—from the time a patient makes an appointment to the time a provider is paid—and everything in between. One way to think of it is in terms of the life cycle of a medical bill. Although there are many ways this process can play out, this post will lay out a common example below:
1. Pre-appointment
For most general care, the first stage of the revenue cycle begins when a patient contacts a provider to set up their appointment. Generally this is when relevant patient information will begin to be collected for the eventual bill, referred to on the financial side of healthcare as a claim.
At this point a provider will determine whether the appointment and procedure will need prior authorization from an insurance company (referred to as the payer). Also, the electronic health record (EHR) used to help generate the claim is created, and will begin to accumulate further detail as the provider sends an eligibility inquiry to check into the patient’s insurance coverage.
2. Point of care
The next step in the process begins when the patient arrives for their appointment. This could include when a patient arrives for an initial consultation, an outpatient procedure, or for a follow-up exam. This could also include a Telehealth appointment.
At any of these events, the provider may charge an up-front cost. One example of this is a co-pay, which is the set amount patients pay after their deductible (if they are insured), however, there are other kinds of payments that fall into this category, too.
3. Claim submission
After the point of care, the provider completes and submits a claim with the appropriate codes to the payer. In order to accomplish that, billing staff must collect all necessary documentation and attach it to the claim. After submitting the claim to the payer, the provider’s team will monitor whether a claim has been been accepted, rejected, or denied.
[ Note: Medical coding refers to the clerical process of translating steps in the patient experience with reference numbers. The codes are normally based on medical documentation, such as a doctor’s notes or laboratory results. These explain to a payer how a patient was diagnosed and treated, and why. This information helps the payer decide how much of an encounter is covered under any given insurance plan, and therefore how much the payer will pay. ]
4. Insurance payment or denial
Once the payer receives the claim, they ensure it contains complete information and agrees with provider and patient records. If there is an error, the claim will be rejected outright and the provider will have to submit a corrected claim.
The payer then begins the review process, referred to as adjudication. Payers evaluate claims for accurate coding and documentation, medical necessity, appropriate authorization, and more. Through this process, the payer decides their financial obligation. Any factor could cause the payer to deny the claim.
If the claim is approved, the payer submits payment to the provider with information explaining details of their decision. If the claim is denied, the provider will need to determine if the original needs to be corrected, or if it makes more sense to appeal the payer’s decision.
Following adjudication, the payer will send an explanation of benefits (EOB) to the patient. This EOB will provide a breakdown of how the patient’s coverage matched up to the charges attached to their care. It is not a billing statement, but it does show what the provider charged the payer, what portion insurance covers, and how much the patient is responsible for.
5. Patient payment
The next phase occurs when the provider sends the patient a statement for their portion of financial responsibility. This stage occurs once the provider and payer have agreed on the details of the claim, what has been paid, and what is still owed.
The last step occurs when a patient pays the balance that they owe the provider for their care. Depending on the amount, the patient may be able pay it all at once, or they might need to work with the provider on a payment plan.
The above example represents one way the lie cycle of a medical bill can play out. Some of the ‘phases’ are often repeated. Because of the complexity of healthcare payments and the parties involved, there is not always a ‘straight line’ from patient care to complete payment. That’s why we call it the revenue cycle, and there are companies that provide systems for its management.
One of EZClaim’s partners, Waystar, aims to simplify and unify healthcare payments. Their technology automates many parts of the billing process laid out above, so it takes less time and energy for providers and their teams, and is more transparent for patients (Click here to learn more about how Waystar automates manual tasks and streamlines workflows.) When the revenue cycle is operating at its most efficient, providers can focus their resources on improving patient care—and that’s a better way forward for everyone!
For more information of how Waystar works together with EZClaim, click here.
[ Article and image provided by Waystar ]
———————————-
ABOUT EZCLAIM:
EZClaim is a medical billing and scheduling software company that provides a best-in-class product, with correspondingly exceptional service and support, and can help improve medical billing revenues. To learn more, visit their website, e-mail them at sales@ezclaim.com, or call a representative today at 877.650.0904.

Sep 10, 2020 | Electronic Billing, Medical Billing Software Blog, Partner
In the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, Telehealth adoption has exploded, and there are six revenue cycle metrics to track.
Many patients are prohibited or reluctant to venture out for on-site care. The combination of relaxed regulations and expanded payment parity for appointments has made virtual meetings easier and more attractive for providers, who are turning to these technologies to stay engaged with patients—and maintain cashflow. Dr. Robert McLean, a former president of the American College of Physicians, recently said, “this crisis has forced us to change how we deliver health care more in 20 days than we had in 20 years.”
A new industry report predicts that the number of Telehealth visits in the US will surpass one billion by the end of the year, and speculates that nearly half of those visits will be related to COVID-19. At Waystar, we have been closely monitoring claim trends and are seeing this growth firsthand. In fact, the volume of Telehealth claims on the Waystar platform has grown by more than 100 times since mid-March. On two particular days in late April, they accounted for more than 15% of our total daily claim volume. Before COVID-19, they would have accounted for less than one percent!
For many providers, this shift will require new revenue cycle strategies to meet growing patient demand without overwhelming clinicians and administrative teams—or already strained operating budgets. It’s important to remember this is still very much an evolving care delivery model with the opportunity for errors on the part of both payers, providers, and administrative staff. For this reason, revenue cycle professionals should diligently monitor claims to ensure proper adjudication, identify learning opportunities, and uncover areas for operational improvement.
Below, we’ve listed six core Telehealth-related metrics you should regularly track to ensure billing accuracy, maximize payer reimbursement, and reduce claim rejections and denials. For more on how to best navigate the evolving telemedicine landscape, check out our resource hub here.
To report on Telehealth-related claims, you’ll first need to identify and isolate claims containing Telehealth procedure codes. See CMS’ Telehealth code list to identify the specific procedure codes and modifiers that apply to your organization.
Payer Analysis:
1. Payer Telehealth claim rejections by volume and/or billed amount
2. Payer Telehealth claim denials by volume and/or billed amount
If your Telehealth claims are being denied or rejected, do you know which specific payers are doing so at the highest rate? Drill down to discover the specific reason codes payers are attaching to rejections and denials so you can better understand payer-specific rules and avoid these oversights in the future. In some cases, you may identify trends that warrant a call to the payer to correct.
Provider Analysis:
3. Telehealth claim volume by the provider
Review this claim volume by individual provider. If you notice providers within your organization generating a much lower volume of Telehealth claims than peers, perhaps they could benefit from additional training on Telehealth technology and use cases.
Ensuring Billing Accuracy:
4. Telehealth claim rejections by biller/team
5. Telehealth claim denials by biller/team
Are certain billing personnel or teams producing higher denial or rejection rates than others? Keep a close eye on these trends and remember most of this is new for everyone. If some team members are seeing more rejections or denials than they should, it could be a great opportunity to hold training and collaborate on strategies for success.
Maximizing Reimbursement:
6. Telehealth claim volume by procedure code
Which Telehealth codes are you using? Each code reimburses at a different rate, so choosing the wrong ones could leave money on the table. Be sure to read up on CMS’ requirements (check out their fact sheet and code list) to ensure you’re choosing the appropriate code(s) on each Telehealth claim.
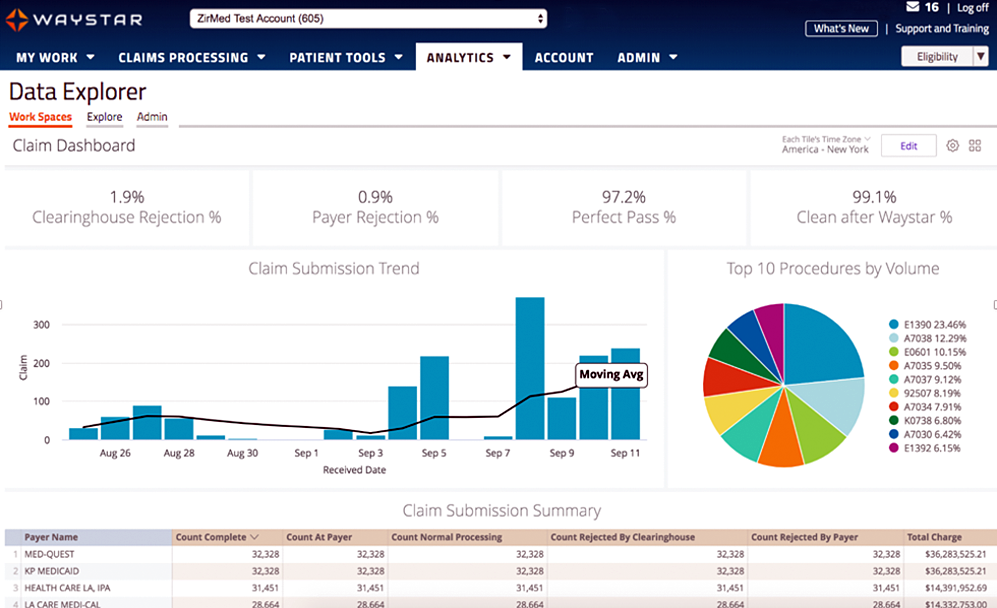
Waystar Analytics
You have all the data you need to drive informed decision making and improve financial performance—you just need the right analytics tool in your corner. Our new Waystar Analytics solution offers a pre-built Telehealth dashboard that can help you easily interpret, share all the metrics above, and track these revenue cycle metrics. Click here to learn more about Waystar Analytics and how it can deliver the insights you need during this time of transition.
[ By Waystar ]

Dec 10, 2019 | Alpha II, Claims, Partner, Revenue
Getting Claims Right the First Time
Getting Claims Right the First Time. Contributed by Timothy Mills, Chief Growth Officer, Alpha II, LLC
The numbers are staggering. Industry averages report that nearly 20% of all claims are denied, rejected, or underpaid. And considering the cost to rework claims — not to mention even higher appeal costs — as many as 60% of returned claims are never resubmitted.
With figures like these, it’s no wonder medical practices continue to face intense financial pressure. As negotiated reimbursements stagnate and operating expenses like rent and salaries continue to increase, the struggle to maintain steady revenue becomes even more crucial. For many practices, conducting reviews of their revenue cycle workflow would show gaps in their claims process. The good news is – these gaps can be bridged with the help of emerging technology.
With a saturated market of coding, billing, and compliance solutions, how do you begin to find the right technology for your practice? When trying to improve revenue integrity, it is important to understand exactly what vendors offer. For example, consider the term “first-pass claims rate,” which is still used by some healthcare IT vendors to represent the number of claims initially accepted by payers. But what is often overlooked is the number of those initially accepted claims that will be denied or underpaid. A better question would be – what percentage of claims are getting paid the first time they are submitted?
The fact is, practices that do not employ the latest clinical coding and editing tools within their revenue cycle are leaving money on the table. This is revenue that is rightfully theirs but is being pursued at high, incremental costs. It’s time to rethink traditional denials management practices, move beyond the “first pass claims rate,” and embrace the future of denial prevention.
It’s your money. Go after it.
Still not convinced that investing in emerging clinical coding and editing software can save your practice money? Let’s see what relying on traditional denials management methods might really be costing you.
Each rejected, denied or underpaid claim represents earned revenue your practice is missing out on. Based on industry reports, the average cost to rework a claim has been pegged at more than $25, and appeal costs can skyrocket to over $100. It’s estimated that as many as two-thirds of all denied claims are recoverable. But practices often weigh the reimbursement amount of a claim against the cost to rework or appeal that claim. For smaller claims, many decide it just isn’t worth the effort, which is why getting claims right the first time should be the ultimate goal.
So how much are practices losing by simply correcting and resubmitting denied claims using traditional denial management methods? Let’s look at an example using figures from an actual mid-sized specialty practice. This practice submits 1,900 claims a month and the average claim is $150. They have a better-than-average denial/rejection rate of 10 percent. Even with that lowered rate, this practice is losing roughly $28,500 a month to unresolved denied claims. If two-thirds of those denied claims are recoverable, they stand to recoup $19,095 in reimbursements after the claims are corrected and resubmitted. Factor in the cost associated with reworking denied claims using the industry average of $25 per claim, and this practice is spending $4,750 in administrative charges alone to recover their own revenue. This brings their actual recovered revenue down to $14,155 per month or almost $170,000 annually. Investing in a comprehensive clinical coding and editing solution is still cheaper than what the practice spends per month when reworking denied claims.
The Alpha II Solution
Are you ready to submit precise claims the first time? Contact Alpha II, a leader in revenue cycle solutions. Our comprehensive clinical claim editing solution, ClaimStaker, covers the entire continuum of care, verifying claim data from the payer’s perspective and allowing for corrections prior to filing.
Check out our Denial Impact Assessment Calculator to see what your denials really cost your practice or contact us today for a free personalized Claims Assessment. See why ClaimStaker does more than clear claims. It gets claims paid.
We work hard to update our blog to keep you up-to-date on what’s happening in the field of medical billing software. If you have a topic you would like to see discussed, please contact us.

 There are five ‘phases’ in the life cycle of a medical bill: Pre-appointment; Point of care; Claim submission; Insurance payment or denial; and Patient payment. This post will overview each of these phases, and could even be considered to be a “101-level” course on Revenue Cycle Management.
There are five ‘phases’ in the life cycle of a medical bill: Pre-appointment; Point of care; Claim submission; Insurance payment or denial; and Patient payment. This post will overview each of these phases, and could even be considered to be a “101-level” course on Revenue Cycle Management.



