Nov 10, 2020 | Medical Billing Software Blog, Partner, Revenue, Support and Training, Waystar
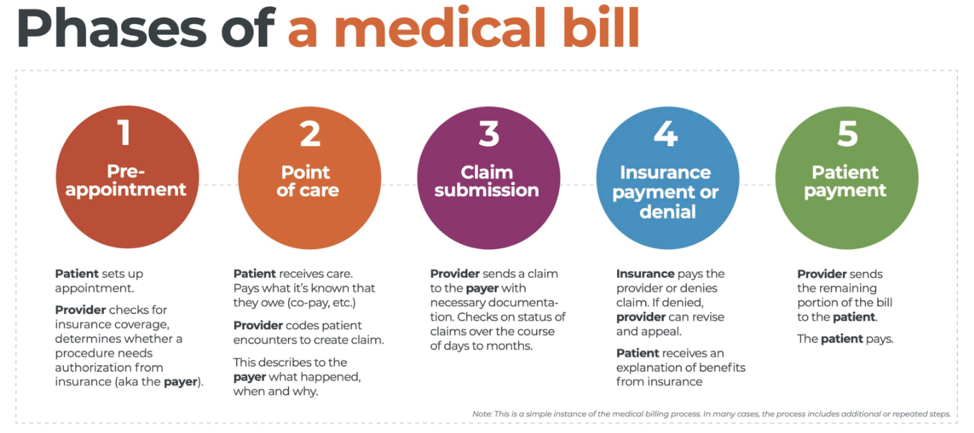
 There are five ‘phases’ in the life cycle of a medical bill: Pre-appointment; Point of care; Claim submission; Insurance payment or denial; and Patient payment. This post will overview each of these phases, and could even be considered to be a “101-level” course on Revenue Cycle Management.
There are five ‘phases’ in the life cycle of a medical bill: Pre-appointment; Point of care; Claim submission; Insurance payment or denial; and Patient payment. This post will overview each of these phases, and could even be considered to be a “101-level” course on Revenue Cycle Management.
With high deductible health plans on the rise, the recent explosion of telehealth appointments due to COVID-19, and many other factors in play, it’s more important than ever for everyone to understand the life cycle of a medical bill, and how the process works. The healthcare revenue cycle is relevant not only to those who work in healthcare, but to the patient, too.
The revenue cycle is the series of processes around healthcare payments—from the time a patient makes an appointment to the time a provider is paid—and everything in between. One way to think of it is in terms of the life cycle of a medical bill. Although there are many ways this process can play out, this post will lay out a common example below:
1. Pre-appointment
For most general care, the first stage of the revenue cycle begins when a patient contacts a provider to set up their appointment. Generally this is when relevant patient information will begin to be collected for the eventual bill, referred to on the financial side of healthcare as a claim.
At this point a provider will determine whether the appointment and procedure will need prior authorization from an insurance company (referred to as the payer). Also, the electronic health record (EHR) used to help generate the claim is created, and will begin to accumulate further detail as the provider sends an eligibility inquiry to check into the patient’s insurance coverage.
2. Point of care
The next step in the process begins when the patient arrives for their appointment. This could include when a patient arrives for an initial consultation, an outpatient procedure, or for a follow-up exam. This could also include a Telehealth appointment.
At any of these events, the provider may charge an up-front cost. One example of this is a co-pay, which is the set amount patients pay after their deductible (if they are insured), however, there are other kinds of payments that fall into this category, too.
3. Claim submission
After the point of care, the provider completes and submits a claim with the appropriate codes to the payer. In order to accomplish that, billing staff must collect all necessary documentation and attach it to the claim. After submitting the claim to the payer, the provider’s team will monitor whether a claim has been been accepted, rejected, or denied.
[ Note: Medical coding refers to the clerical process of translating steps in the patient experience with reference numbers. The codes are normally based on medical documentation, such as a doctor’s notes or laboratory results. These explain to a payer how a patient was diagnosed and treated, and why. This information helps the payer decide how much of an encounter is covered under any given insurance plan, and therefore how much the payer will pay. ]
4. Insurance payment or denial
Once the payer receives the claim, they ensure it contains complete information and agrees with provider and patient records. If there is an error, the claim will be rejected outright and the provider will have to submit a corrected claim.
The payer then begins the review process, referred to as adjudication. Payers evaluate claims for accurate coding and documentation, medical necessity, appropriate authorization, and more. Through this process, the payer decides their financial obligation. Any factor could cause the payer to deny the claim.
If the claim is approved, the payer submits payment to the provider with information explaining details of their decision. If the claim is denied, the provider will need to determine if the original needs to be corrected, or if it makes more sense to appeal the payer’s decision.
Following adjudication, the payer will send an explanation of benefits (EOB) to the patient. This EOB will provide a breakdown of how the patient’s coverage matched up to the charges attached to their care. It is not a billing statement, but it does show what the provider charged the payer, what portion insurance covers, and how much the patient is responsible for.
5. Patient payment
The next phase occurs when the provider sends the patient a statement for their portion of financial responsibility. This stage occurs once the provider and payer have agreed on the details of the claim, what has been paid, and what is still owed.
The last step occurs when a patient pays the balance that they owe the provider for their care. Depending on the amount, the patient may be able pay it all at once, or they might need to work with the provider on a payment plan.
The above example represents one way the lie cycle of a medical bill can play out. Some of the ‘phases’ are often repeated. Because of the complexity of healthcare payments and the parties involved, there is not always a ‘straight line’ from patient care to complete payment. That’s why we call it the revenue cycle, and there are companies that provide systems for its management.
One of EZClaim’s partners, Waystar, aims to simplify and unify healthcare payments. Their technology automates many parts of the billing process laid out above, so it takes less time and energy for providers and their teams, and is more transparent for patients (Click here to learn more about how Waystar automates manual tasks and streamlines workflows.) When the revenue cycle is operating at its most efficient, providers can focus their resources on improving patient care—and that’s a better way forward for everyone!
For more information of how Waystar works together with EZClaim, click here.
[ Article and image provided by Waystar ]
———————————-
ABOUT EZCLAIM:
EZClaim is a medical billing and scheduling software company that provides a best-in-class product, with correspondingly exceptional service and support, and can help improve medical billing revenues. To learn more, visit their website, e-mail them at sales@ezclaim.com, or call a representative today at 877.650.0904.

Aug 11, 2020 | Administrative Safeguards, Live Compliance, Partner
Failing to implement HIPAA causes a large fine for a small-town North Carolina health services provider. They were fined $25,000 for multiple, easily avoidable, HIPAA violations for “longstanding, systemic non-compliance” with the HIPAA Security Rule. [ Note: The provider is a part of a health center that offers discounted medical services to the underserved population in rural NC, and the fines were reduced in consideration of this, but it still resulted in a significant monetary loss ].
In 2011, Metropolitan Community Health Services (Metro), doing business as Agape Health Services, filed a breach report regarding “the impermissible disclosure of protected health information to an unknown email account.” The breach affected over 1,200 patients!
In addition to the large monetary penalty, the practice is required to develop and adopt a corrective action plan (which includes two years of thorough monitoring) after the Office for Civil Rights (OCR) discovered that Metro failed to conduct a thorough and comprehensive HIPAA Security Risk Assessment and Analysis. In addition, Metro did not implement a single HIPAA Security Rule Policy and Procedure for the health center. Possibly worst of all, Metro failed to provide workforce members with HIPAA Privacy and Security Awareness training until 2016!
Patients must trust with who they share their personal, private, and protected health information. A breach such as this is obviously devastating for the patient, in addition to their doctor’s reputation. So, how can physicians ensure that they are meeting the HIPAA requirements and have proper safeguards in place to avoid this sort of breach?
First off, an accurate and thorough Security Risk Assessment and Analysis must be conducted to expose and target any potential administrative, physical, and technical vulnerabilities. Doing so highlights any major flaws in a practice’s administrative and technical safeguards, and accentuates the policies and procedures that the practice needs to implement.
In addition to that, the designated HIPAA Privacy and Security Officer must ensure that ALL employees complete HIPAA Workforce training. All employees of the practice, including the physicians, must take HIPAA training to ensure employees have a clear understanding of the HIPAA Privacy Rule and actionable policies and procedures.
So, remember, healthcare organizations and their vendors have a responsibility to be HIPAA compliant, and that starts by performing, updating, or reviewing an accurate and thorough Security Risk Assessment covering your technical, administrative, and physical safeguards. This will help uncover any vulnerabilities, and help you understand what information is being transmitted, shared, and how it is being transmitted.
TAKEAWAYS AND THINGS TO CONSIDER:
- Complete a Security Risk Assessment and establish a Corrective Action Plan that is accurate and thorough.
Remediate any potential risks or vulnerabilities.
- A Security Risk Assessment will target vulnerabilities related to what is potentially exposing Protected Health Information (PHI)
- Develop actionable policies and procedures that clearly outline disclosures of PHI
- Ensure all employees have a clear understanding of the HIPAA Privacy rule and its policies and procedures
Live Compliance provides everything you need to become and maintain your organization’s HIPAA compliance requirements. All policies and procedures can be edited and shared directly with staff from your staff portal. Training are delivered and monitored within your portal, can be customized, role-based, and be accessed anytime and from anywhere. You can also easily send and monitor HIPAA training with one click.
Failing to implement HIPAA can cause tremendous problems and use precious resources and time to implement. Live Compliance makes it 10X easier than trying to do it on your own.
So, take advantage of Live Compliance’s FREE Organization Needs Assessment to understand your immediate compliance needs. For additional details, e-mail Jim Johnson (at jim@livecompliance.com), call (980) 999-1585, or visit their website at livecompliance.com/oa
Live Compliance is a partner of EZClaim, a medical billing software company. For more details about their solutions, visit their website at ezclaim.com.
[ Written by Jim Johnson, President of Live Compliance ]
Apr 13, 2020 | Health eFilings, Partner
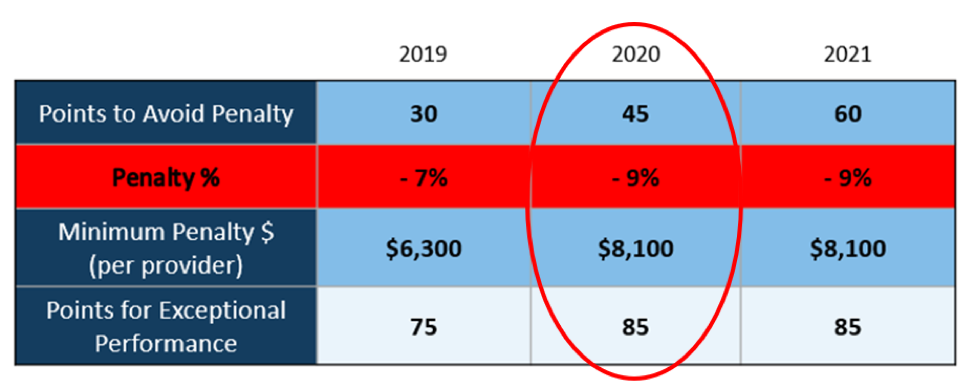
There WILL NOT be any changes to the MIPS Program in 2020, so all payers must be submitted and a minimum of 45 points must be earned to avoid the 9% penalty.
On March 23, 2020, CMS made it perfectly clear that MIPS Program is not going away in 2020. It also reiterated that the data requirements and thresholds in place for the 2020 program have not changed. Additionally, Promoting Interoperability and Improvement Activities must be done for the required durations, or no points will be earned for those categories.
To put this in context, while the stakes have been raised every year, the final ruling for the 2020 reporting period is the most complex to-date, further increasing the stress, burden, and financial risk for over 900,000 clinicians who bill Medicare Part B. Failure to comply or earn enough points for the 2020 reporting period will result in an automatic 9% penalty on every Medicare Part B claim paid for an entire year. This equates to a minimum of a $8,100 per provider hit to the bottom line.
Given the unprecedented time when everyone’s bottom line is at risk, now is the time to get a handle on what’s at risk with the MIPS program and proactively engage to ensure your bottom line is not further jeopardized by being assessed a 9% penalty. It can be challenging to know exactly what you need to do to earn points, optimize your score, and protect your Medicare reimbursements, as there are many commonly misunderstood aspects and nuances with the MIPS program.
So, with what is at stake and the inherent complexity in earning points, it is critical that you select the right methodology and partner who can help you maximize reimbursements and protect your bottom line. Not all reporting methodologies are the same.
Health eFilings‘ CEHRT is the best choice for a reporting partner. Their cloud-based ONC-certified software fully automates the process and does all the work without any IT resources, administrative support, and workflow changes from the practice. Health eFilings service is an end-to-end electronic solution that will save significant time, be a turn-key submission process, and maximize the financial upside for providers.
As more than 25% of the 2020 reporting period is behind us, now is the time to act while there is still plenty of time to positively impact your results and points earned.
Health eFiling provides the nation’s only fully automated solution for MIPS compliance and is integrated with EZclaim’s billing solution. Click on the following link for more details: https://healthefilings.com/ezclaim
[Contribution by Sarah Reiter with the Senior VP of Strategic Partnerships]

 There are five ‘phases’ in the life cycle of a medical bill: Pre-appointment; Point of care; Claim submission; Insurance payment or denial; and Patient payment. This post will overview each of these phases, and could even be considered to be a “101-level” course on Revenue Cycle Management.
There are five ‘phases’ in the life cycle of a medical bill: Pre-appointment; Point of care; Claim submission; Insurance payment or denial; and Patient payment. This post will overview each of these phases, and could even be considered to be a “101-level” course on Revenue Cycle Management.


